Section 10 Computational Thinking
Chapter 50 - Thinking logically, thinking currently
Different methods of Designing Algorithms
- Flow charts : A diagram of the sequence of movements or actions of people or things involved in a complex system or activity.
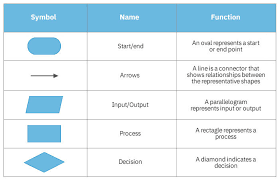
- Pseudocode: is an informal, high-level description of a computer program or algorithm, often using natural language mixed with basic
programming concepts to outline functionality and logic without strict syntax.

Thinking Currently
- Concurrent computing: Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed concurrently—during overlapping
time periods—instead of sequentially—with one completing before the next starts.
- Parrallel computing: Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously
- Current Processing: takes place when several processes are running, with each in turn being given a slice of processor time. This gives the appearance that several tasks are being performed simultaneously, even though only one processor is being used.
Advantages of Current Processing
- Increased program throughput
- Time that would be wasted by the processor waiting for the user to input data or look at output is
used on another task
Disadvantages of Current Processing
- If a large number of users are all trying to run programs, and some of these
involve a lot of computation, these programs wil take longer to complete
Advantages of Parallel Processing
- Enable several tasks to be performed simultaneously by different processors. It
can speed up processing enormously when repetitive calculations need to be performed on large
amounts of data
- Graphics processors can quickly render a3-D object by working simultaneously on individual
components of the graphic
Disadvantages of Parallel Processing
- parallel processing has limitations; there is an overhead in coordinating the processors and some
tasks may run faster with a single processor than with multiple processors.
Chapter 51 Problem Recognition
Methods of Problem Solving
- Enumeration - Listing all cases
- Simulation - is the process of designing a model of a real system in order to understand the behaviour of the system
- Theoretical Approach -
- Divide and Conquer - divide and conquer is an algorithm design paradigm. A divide-and-conquer algorithm recursively breaks down a problem
into two or more sub-problems of the same or related type, until these become simple enough to be solved directly.
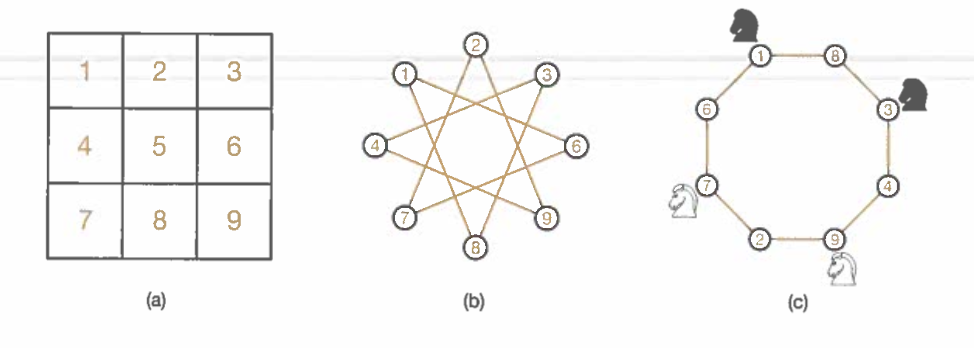
- Problem Abstraction(shown through images)
Normal:

Abstracted:
Chapter 52 Problem Solving
Visualisation
- Visualistion is the use of interactive, sensory representations, typically visual, of abstract data to reinforce cognition, hypothesis
building, and reasoning.
Backtracking
- Backtracking is a method of trying out different sequences until you come accorss that leads you to the solution
- When you would use backtracking:
- You dont have enough info to know which is the best route
- Each decision leads to a new set of choices
- Depth Searching a graph

